Microsoft Network Policy Server Mac Authentication
- Microsoft Network Policy Server Mac Authentication Code
- Network Policy Server Windows 10
- Microsoft Network Policy Server Mac Authentication Download
- Microsoft Network Client
- Windows Server Network Policy Server
This article provides details for integrating your Remote Desktop Gateway infrastructure with Azure Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) using the Network Policy Server (NPS) extension for Microsoft Azure.
Internet Authentication Service (IAS) was renamed Network Policy Server (NPS). Internet Authentication Service. Internet Authentication Service is the Microsoft implementation of a RADIUS server and proxy. Internet Authentication Service supports two API sets: Network Policy Server Extensions API and Server Data Objects API. Network Policy Server (NPS) allows you to create and enforce organization-wide network access policies for connection request authentication and authorization.
The Network Policy Server (NPS) extension for Azure allows customers to safeguard Remote Authentication Dial-In User Service (RADIUS) client authentication using Azure's cloud-based Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA). This solution provides two-step verification for adding a second layer of security to user sign-ins and transactions.
This article provides step-by-step instructions for integrating the NPS infrastructure with Azure MFA using the NPS extension for Azure. This enables secure verification for users attempting to sign in to a Remote Desktop Gateway.
Note
This article should not be used with MFA Server deployments and should only be used with Azure MFA (Cloud-based) deployments.
The Network Policy and Access Services (NPS) gives organizations the ability to do the following:
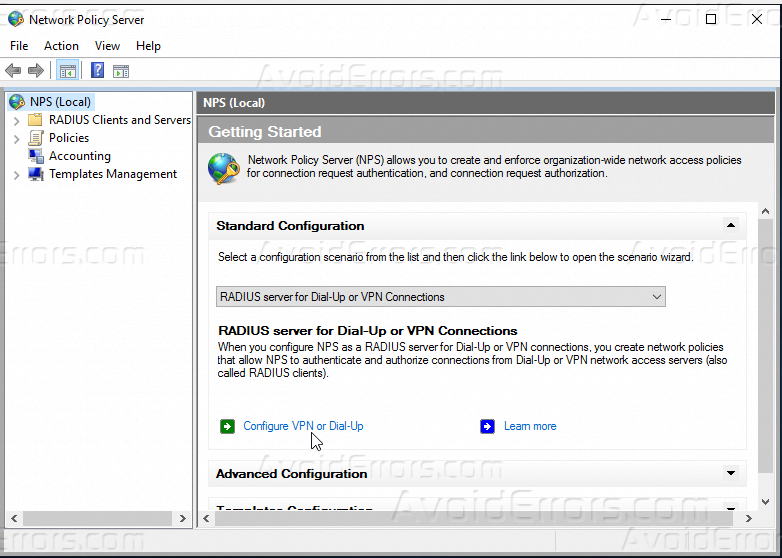
- Define central locations for the management and control of network requests by specifying who can connect, what times of day connections are allowed, the duration of connections, and the level of security that clients must use to connect, and so on. Rather than specifying these policies on each VPN or Remote Desktop (RD) Gateway server, these policies can be specified once in a central location. The RADIUS protocol provides the centralized Authentication, Authorization, and Accounting (AAA).
- Establish and enforce Network Access Protection (NAP) client health policies that determine whether devices are granted unrestricted or restricted access to network resources.
- Provide a means to enforce authentication and authorization for access to 802.1x-capable wireless access points and Ethernet switches.
Typically, organizations use NPS (RADIUS) to simplify and centralize the management of VPN policies. However, many organizations also use NPS to simplify and centralize the management of RD Desktop Connection Authorization Policies (RD CAPs).
Organizations can also integrate NPS with Azure MFA to enhance security and provide a high level of compliance. This helps ensure that users establish two-step verification to sign in to the Remote Desktop Gateway. For users to be granted access, they must provide their username/password combination along with information that the user has in their control. This information must be trusted and not easily duplicated, such as a cell phone number, landline number, application on a mobile device, and so on. RDG currently supports phone call and push notifications from Microsoft authenticator app methods for 2FA. For more information about supported authentication methods see the section Determine which authentication methods your users can use.
Prior to the availability of the NPS extension for Azure, customers who wished to implement two-step verification for integrated NPS and Azure MFA environments had to configure and maintain a separate MFA Server in the on-premises environment as documented in Remote Desktop Gateway and Azure Multi-Factor Authentication Server using RADIUS.
The availability of the NPS extension for Azure now gives organizations the choice to deploy either an on-premises based MFA solution or a cloud-based MFA solution to secure RADIUS client authentication.
Authentication Flow
For users to be granted access to network resources through a Remote Desktop Gateway, they must meet the conditions specified in one RD Connection Authorization Policy (RD CAP) and one RD Resource Authorization Policy (RD RAP). RD CAPs specify who is authorized to connect to RD Gateways. RD RAPs specify the network resources, such as remote desktops or remote apps, that the user is allowed to connect to through the RD Gateway.
An RD Gateway can be configured to use a central policy store for RD CAPs. RD RAPs cannot use a central policy, as they are processed on the RD Gateway. An example of an RD Gateway configured to use a central policy store for RD CAPs is a RADIUS client to another NPS server that serves as the central policy store.
When the NPS extension for Azure is integrated with the NPS and Remote Desktop Gateway, the successful authentication flow is as follows:
- The Remote Desktop Gateway server receives an authentication request from a remote desktop user to connect to a resource, such as a Remote Desktop session. Acting as a RADIUS client, the Remote Desktop Gateway server converts the request to a RADIUS Access-Request message and sends the message to the RADIUS (NPS) server where the NPS extension is installed.
- The username and password combination is verified in Active Directory and the user is authenticated.
- If all the conditions as specified in the NPS Connection Request and the Network Policies are met (for example, time of day or group membership restrictions), the NPS extension triggers a request for secondary authentication with Azure MFA.
- Azure MFA communicates with Azure AD, retrieves the user's details, and performs the secondary authentication using supported methods.
- Upon success of the MFA challenge, Azure MFA communicates the result to the NPS extension.
- The NPS server, where the extension is installed, sends a RADIUS Access-Accept message for the RD CAP policy to the Remote Desktop Gateway server.
- The user is granted access to the requested network resource through the RD Gateway.
Prerequisites
This section details the prerequisites necessary before integrating Azure MFA with the Remote Desktop Gateway. Before you begin, you must have the following prerequisites in place.
- Remote Desktop Services (RDS) infrastructure
- Azure MFA License
- Windows Server software
- Network Policy and Access Services (NPS) role
- Azure Active Directory synched with on-premises Active Directory
- Azure Active Directory GUID ID
Remote Desktop Services (RDS) infrastructure
You must have a working Remote Desktop Services (RDS) infrastructure in place. If you do not, then you can quickly create this infrastructure in Azure using the following quickstart template: Create Remote Desktop Session Collection deployment.
If you wish to manually create an on-premises RDS infrastructure quickly for testing purposes, follow the steps to deploy one.Learn more: Deploy RDS with Azure quickstart and Basic RDS infrastructure deployment.
Azure MFA License
Required is a license for Azure MFA, which is available through Azure AD Premium or other bundles that include it. Consumption-based licenses for Azure MFA, such as per user or per authentication licenses, are not compatible with the NPS extension. For more information, see How to get Azure Multi-Factor Authentication. For testing purposes, you can use a trial subscription.
Windows Server software
The NPS extension requires Windows Server 2008 R2 SP1 or above with the NPS role service installed. All the steps in this section were performed using Windows Server 2016.
Network Policy and Access Services (NPS) role
The NPS role service provides the RADIUS server and client functionality as well as Network Access Policy health service. This role must be installed on at least two computers in your infrastructure: The Remote Desktop Gateway and another member server or domain controller. By default, the role is already present on the computer configured as the Remote Desktop Gateway. You must also install the NPS role on at least on another computer, such as a domain controller or member server.
For information on installing the NPS role service Windows Server 2012 or older, see Install a NAP Health Policy Server. For a description of best practices for NPS, including the recommendation to install NPS on a domain controller, see Best Practices for NPS.
Azure Active Directory synched with on-premises Active Directory
To use the NPS extension, on-premises users must be synced with Azure AD and enabled for MFA. This section assumes that on-premises users are synched with Azure AD using AD Connect. For information on Azure AD connect, see Integrate your on-premises directories with Azure Active Directory.
Azure Active Directory GUID ID
To install NPS extension, you need to know the GUID of the Azure AD. Instructions for finding the GUID of the Azure AD are provided below.
Configure Multi-Factor Authentication
This section provides instructions for integrating Azure MFA with the Remote Desktop Gateway. As an administrator, you must configure the Azure MFA service before users can self-register their multi-factor devices or applications.
Follow the steps in Getting started with Azure Multi-Factor Authentication in the cloud to enable MFA for your Azure AD users.
Configure accounts for two-step verification
Once an account has been enabled for MFA, you cannot sign in to resources governed by the MFA policy until you have successfully configured a trusted device to use for the second authentication factor and have authenticated using two-step verification.
Follow the steps in What does Azure Multi-Factor Authentication mean for me? to understand and properly configure your devices for MFA with your user account.
Install and configure NPS extension
This section provides instructions for configuring RDS infrastructure to use Azure MFA for client authentication with the Remote Desktop Gateway.
Acquire Azure Active Directory GUID ID
As part of the configuration of the NPS extension, you need to supply admin credentials and the Azure AD ID for your Azure AD tenant. The following steps show you how to get the tenant ID.
Sign in to the Azure portal as the global administrator of the Azure tenant.
In the Azure portal menu, select Azure Active Directory, or search for and select Azure Active Directory from any page.
Select Properties.
In the Properties blade, beside the Directory ID, click the Copy icon, as shown below, to copy the ID to clipboard.
Install the NPS extension
Install the NPS extension on a server that has the Network Policy and Access Services (NPS) role installed. This functions as the RADIUS server for your design.
Important
Be sure you do not install the NPS extension on your Remote Desktop Gateway server.
- Download the NPS extension.
- Copy the setup executable file (NpsExtnForAzureMfaInstaller.exe) to the NPS server.
- On the NPS server, double-click NpsExtnForAzureMfaInstaller.exe. If prompted, click Run.
- In the NPS Extension For Azure MFA Setup dialog box, review the software license terms, check I agree to the license terms and conditions, and click Install.
- In the NPS Extension For Azure MFA Setup dialog box, click Close.
Configure certificates for use with the NPS extension using a PowerShell script
Next, you need to configure certificates for use by the NPS extension to ensure secure communications and assurance. The NPS components include a Windows PowerShell script that configures a self-signed certificate for use with NPS.
The script performs the following actions:
- Creates a self-signed certificate
- Associates public key of certificate to service principal on Azure AD
- Stores the cert in the local machine store
- Grants access to the certificate's private key to the network user
- Restarts Network Policy Server service
If you want to use your own certificates, you need to associate the public key of your certificate to the service principal on Azure AD, and so on.
To use the script, provide the extension with your Azure AD Admin credentials and the Azure AD tenant ID that you copied earlier. Run the script on each NPS server where you installed the NPS extension. Then do the following:
Open an administrative Windows PowerShell prompt.
At the PowerShell prompt, type
cd 'c:Program FilesMicrosoftAzureMfaConfig', and press ENTER.Type
.AzureMfaNpsExtnConfigSetup.ps1, and press ENTER. The script checks to see if the Azure Active Directory PowerShell module is installed. If not installed, the script installs the module for you.After the script verifies the installation of the PowerShell module, it displays the Azure Active Directory PowerShell module dialog box. In the dialog box, enter your Azure AD admin credentials and password, and click Sign In.
When prompted, paste the Directory ID you copied to the clipboard earlier, and press ENTER.
The script creates a self-signed certificate and performs other configuration changes. The output should be like the image shown below.
Configure NPS components on Remote Desktop Gateway
In this section, you configure the Remote Desktop Gateway connection authorization policies and other RADIUS settings.
The authentication flow requires that RADIUS messages be exchanged between the Remote Desktop Gateway and the NPS server where the NPS extension is installed. This means that you must configure RADIUS client settings on both Remote Desktop Gateway and the NPS server where the NPS extension is installed.
Configure Remote Desktop Gateway connection authorization policies to use central store
Remote Desktop connection authorization policies (RD CAPs) specify the requirements for connecting to a Remote Desktop Gateway server. RD CAPs can be stored locally (default) or they can be stored in a central RD CAP store that is running NPS. To configure integration of Azure MFA with RDS, you need to specify the use of a central store.
On the RD Gateway server, open Server Manager.
On the menu, click Tools, point to Remote Desktop Services, and then click Remote Desktop Gateway Manager.
In the RD Gateway Manager, right-click [Server Name] (Local), and click Properties.
In the Properties dialog box, select the RD CAP Store tab.
On the RD CAP Store tab, select Central server running NPS.
In the Enter a name or IP address for the server running NPS field, type the IP address or server name of the server where you installed the NPS extension.
Click Add.
Microsoft expression web 4 free version for mac. Microsoft expression web free download - Microsoft Expression Media, Microsoft Outlook Express, Microsoft Entourage 2008 Web Services Edition, and many more programs. Microsoft Expression Web 4 (Free Version) Language: English. Expression Web is a full-featured professional tool for designing, developing, and publishing compelling, feature-rich websites that conform to web standards. Microsoft Expression Community website; Expression Web Forums. Skype for Business on Mac 04 DirectX. Microsoft expression web 4 free download - Microsoft Expression Media, Microsoft Outlook Express, 3ivx Delta 4, and many more programs. Dec 20, 2012.NET Framework 4.0 Silverlight 4.0 Support for Microsoft DirectX® 9.0 graphics with Windows Vista Display Driver Model (WDDM) Driver, 128 MB of graphics RAM or more, Pixel Shader 3.0 in hardware, 32-bits per pixel. Microsoft Expression Web for Mac. Microsoft Expression Web by Microsoft Corporation is an application that can help you design, develop and publish websites and it offers support for various programming languages, including HTML, CSS, JavaScript or PHP.
In the Shared Secret dialog box, enter a shared secret, and then click OK. Ensure you record this shared secret and store the record securely.
Note
Shared secret is used to establish trust between the RADIUS servers and clients. Create a long and complex secret.
Click OK to close the dialog box.
Configure RADIUS timeout value on Remote Desktop Gateway NPS
To ensure there is time to validate users' credentials, perform two-step verification, receive responses, and respond to RADIUS messages, it is necessary to adjust the RADIUS timeout value.
On the RD Gateway server, open Server Manager. On the menu, click Tools, and then click Network Policy Server.
In the NPS (Local) console, expand RADIUS Clients and Servers, and select Remote RADIUS Server.
In the details pane, double-click TS GATEWAY SERVER GROUP.
Note
This RADIUS Server Group was created when you configured the central server for NPS policies. The RD Gateway forwards RADIUS messages to this server or group of servers, if more than one in the group.
In the TS GATEWAY SERVER GROUP Properties dialog box, select the IP address or name of the NPS server you configured to store RD CAPs, and then click Edit.
In the Edit RADIUS Server dialog box, select the Load Balancing tab.
In the Load Balancing tab, in the Number of seconds without response before request is considered dropped field, change the default value from 3 to a value between 30 and 60 seconds.
In the Number of seconds between requests when server is identified as unavailable field, change the default value of 30 seconds to a value that is equal to or greater than the value you specified in the previous step.
Click OK two times to close the dialog boxes.
Verify Connection Request Policies
By default, when you configure the RD Gateway to use a central policy store for connection authorization policies, the RD Gateway is configured to forward CAP requests to the NPS server. The NPS server with the Azure MFA extension installed, processes the RADIUS access request. The following steps show you how to verify the default connection request policy.
On the RD Gateway, in the NPS (Local) console, expand Policies, and select Connection Request Policies.
Double-click TS GATEWAY AUTHORIZATION POLICY.
In the TS GATEWAY AUTHORIZATION POLICY properties dialog box, click the Settings tab.
On Settings tab, under Forwarding Connection Request, click Authentication. RADIUS client is configured to forward requests for authentication.
Click Cancel.
Note
For more information about creating a connection request policy see the article, Configure connection request policies documentation for the same.
Configure NPS on the server where the NPS extension is installed
The NPS server where the NPS extension is installed needs to be able to exchange RADIUS messages with the NPS server on the Remote Desktop Gateway. To enable this message exchange, you need to configure the NPS components on the server where the NPS extension service is installed.
Register Server in Active Directory
To function properly in this scenario, the NPS server needs to be registered in Active Directory.
On the NPS server, open Server Manager.
In Server Manager, click Tools, and then click Network Policy Server.
In the Network Policy Server console, right-click NPS (Local), and then click Register server in Active Directory.
Click OK two times.
Leave the console open for the next procedure.
Create and configure RADIUS client
The Remote Desktop Gateway needs to be configured as a RADIUS client to the NPS server.
On the NPS server where the NPS extension is installed, in the NPS (Local) console, right-click RADIUS Clients and click New.
In the New RADIUS Client dialog box, provide a friendly name, such as Gateway, and the IP address or DNS name of the Remote Desktop Gateway server.
In the Shared secret and the Confirm shared secret fields, enter the same secret that you used before.
Click OK to close the New RADIUS Client dialog box.
Configure Network Policy
Recall that the NPS server with the Azure MFA extension is the designated central policy store for the Connection Authorization Policy (CAP). Therefore, you need to implement a CAP on the NPS server to authorize valid connections requests.
On the NPS Server, open the NPS (Local) console, expand Policies, and click Network Policies.
Right-click Connections to other access servers, and click Duplicate Policy.
Right-click Copy of Connections to other access servers, and click Properties.
In the Copy of Connections to other access servers dialog box, in Policy name, enter a suitable name, such as RDG_CAP. Check Policy enabled, and select Grant access. Optionally, in Type of network access server, select Remote Desktop Gateway, or you can leave it as Unspecified.
Click the Constraints tab, and check Allow clients to connect without negotiating an authentication method.
Optionally, click the Conditions tab and add conditions that must be met for the connection to be authorized, for example, membership in a specific Windows group.
Click OK. When prompted to view the corresponding Help topic, click No.
Ensure that your new policy is at the top of the list, that the policy is enabled, and that it grants access.
Verify configuration
To verify the configuration, you need to sign in to the Remote Desktop Gateway with a suitable RDP client. Be sure to use an account that is allowed by your Connection Authorization Policies and is enabled for Azure MFA.
As show in the image below, you can use the Remote Desktop Web Access page.
Upon successfully entering your credentials for primary authentication, the Remote Desktop Connect dialog box shows a status of Initiating remote connection, as shown below.
If you successfully authenticate with the secondary authentication method you previously configured in Azure MFA, you are connected to the resource. However, if the secondary authentication is not successful, you are denied access to the resource.
In the example below, the Authenticator app on a Windows phone is used to provide the secondary authentication.
Once you have successfully authenticated using the secondary authentication method, you are logged into the Remote Desktop Gateway as normal. However, because you are required to use a secondary authentication method using a mobile app on a trusted device, the sign in process is more secure than it would be otherwise.
View Event Viewer logs for successful logon events
To view the successful sign-in events in the Windows Event Viewer logs, you can issue the following Windows PowerShell command to query the Windows Terminal Services and Windows Security logs.
To query successful sign-in events in the Gateway operational logs (Event ViewerApplications and Services LogsMicrosoftWindowsTerminalServices-GatewayOperational), use the following PowerShell commands:
Get-WinEvent -Logname Microsoft-Windows-TerminalServices-Gateway/Operational where {$_.ID -eq '300'} FL- This command displays Windows events that show the user met resource authorization policy requirements (RD RAP) and was granted access.
Get-WinEvent -Logname Microsoft-Windows-TerminalServices-Gateway/Operational where {$_.ID -eq '200'} FL- This command displays the events that show when user met connection authorization policy requirements.
You can also view this log and filter on event IDs, 300 and 200. To query successful logon events in the Security event viewer logs, use the following command:
Get-WinEvent -Logname Security where {$_.ID -eq '6272'} FL- This command can be run on either the central NPS or the RD Gateway Server.
You can also view the Security log or the Network Policy and Access Services custom view, as shown below:
On the server where you installed the NPS extension for Azure MFA, you can find Event Viewer application logs specific to the extension at Application and Services LogsMicrosoftAzureMfa.
Troubleshoot Guide
If the configuration is not working as expected, the first place to start to troubleshoot is to verify that the user is configured to use Azure MFA. Have the user connect to the Azure portal. If users are prompted for secondary verification and can successfully authenticate, you can eliminate an incorrect configuration of Azure MFA.
If Azure MFA is working for the user(s), you should review the relevant Event logs. These include the Security Event, Gateway operational, and Azure MFA logs that are discussed in the previous section.
Below is an example output of Security log showing a failed logon event (Event ID 6273).
Below is a related event from the AzureMFA logs:
To perform advanced troubleshoot options, consult the NPS database format log files where the NPS service is installed. These log files are created in %SystemRoot%System32Logs folder as comma-delimited text files.
For a description of these log files, see Interpret NPS Database Format Log Files. The entries in these log files can be difficult to interpret without importing them into a spreadsheet or a database. You can find several IAS parsers online to assist you in interpreting the log files.
The image below shows the output of one such downloadable shareware application.
Finally, for additional troubleshoot options, you can use a protocol analyzer, such Microsoft Message Analyzer.
The image below from Microsoft Message Analyzer shows network traffic filtered on RADIUS protocol that contains the user name CONTOSOAliceC.
Microsoft Network Policy Server Mac Authentication Code
Next steps
-->Applies to: Windows Server (Semi-Annual Channel), Windows Server 2016
You can use this topic to learn about best practices for deploying and managing Network Policy Server (NPS).
The following sections provide best practices for different aspects of your NPS deployment.
Accounting
Following are the best practices for NPS logging.
There are two types of accounting, or logging, in NPS:
Event logging for NPS. You can use event logging to record NPS events in the system and security event logs. This is used primarily for auditing and troubleshooting connection attempts.
Logging user authentication and accounting requests. You can log user authentication and accounting requests to log files in text format or database format, or you can log to a stored procedure in a SQL Server 2000 database. Request logging is used primarily for connection analysis and billing purposes, and is also useful as a security investigation tool, providing you with a method of tracking down the activity of an attacker.
To make the most effective use of NPS logging:
Turn on logging (initially) for both authentication and accounting records. Modify these selections after you have determined what is appropriate for your environment.
Microsoft office mac update download. Ensure that event logging is configured with a capacity that is sufficient to maintain your logs.
Back up all log files on a regular basis because they cannot be recreated when they are damaged or deleted.
Use the RADIUS Class attribute to both track usage and simplify the identification of which department or user to charge for usage. Although the automatically generated Class attribute is unique for each request, duplicate records might exist in cases where the reply to the access server is lost and the request is resent. You might need to delete duplicate requests from your logs to accurately track usage.
If your network access servers and RADIUS proxy servers periodically send fictional connection request messages to NPS to verify that the NPS is online, use the ping user-name registry setting. This setting configures NPS to automatically reject these false connection requests without processing them. In addition, NPS does not record transactions involving the fictional user name in any log files, which makes the event log easier to interpret.
Disable NAS Notification Forwarding. You can disable the forwarding of start and stop messages from network access servers (NASs) to members of a remote RADIUS server group THAT IS configured in NPS. For more information, see Disable NAS Notification Forwarding.
For more information, see Configure Network Policy Server Accounting.
- To provide failover and redundancy with SQL Server logging, place two computers running SQL Server on different subnets. Use the SQL Server Create Publication Wizard to set up database replication between the two servers. For more information, see SQL Server Technical Documentation and SQL Server Replication.
Authentication
Following are the best practices for authentication.
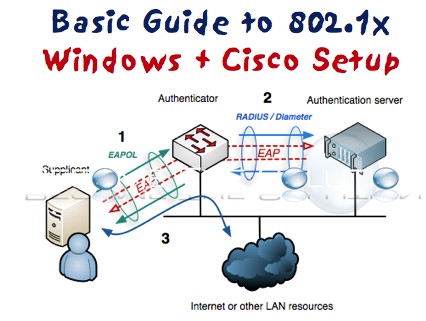
- Use certificate-based authentication methods such as Protected Extensible Authentication Protocol (PEAP) and Extensible Authentication Protocol (EAP) for strong authentication. Do not use password-only authentication methods because they are vulnerable to a variety of attacks and are not secure. For secure wireless authentication, using PEAP-MS-CHAP v2 is recommended, because the NPS proves its identity to wireless clients by using a server certificate, while users prove their identity with their user name and password. For more information about using NPS in your wireless deployment, see Deploy Password-Based 802.1X Authenticated Wireless Access.
- Deploy your own certification authority (CA) with Active Directory速 Certificate Services (AD CS) when you use strong certificate-based authentication methods, such as PEAP and EAP, that require the use of a server certificate on NPSs. You can also use your CA to enroll computer certificates and user certificates. For more information on deploying server certificates to NPS and Remote Access servers, see Deploy Server Certificates for 802.1X Wired and Wireless Deployments.
Important
Network Policy Server (NPS) does not support the use of the Extended ASCII characters within passwords.
Client computer configuration
Following are the best practices for client computer configuration.
- Automatically configure all of your domain member 802.1X client computers by using Group Policy. For more information, see the section 'Configure Wireless Network (IEEE 802.11) Policies' in the topic Wireless Access Deployment.
Installation suggestions
Following are the best practices for installing NPS.
Before installing NPS, install and test each of your network access servers using local authentication methods before you configure them as RADIUS clients in NPS.
After you install and configure NPS, save the configuration by using the Windows PowerShell command Export-NpsConfiguration. Save the NPS configuration with this command each time you reconfigure the NPS.
Caution
- The exported NPS configuration file contains unencrypted shared secrets for RADIUS clients and members of remote RADIUS server groups. Because of this, make sure that you save the file to a secure location.
- The export process does not include logging settings for Microsoft SQL Server in the exported file. If you import the exported file to another NPS, you must manually configure SQL Server Logging on the new server.
Performance tuning NPS
Following are the best practices for performance tuning NPS.
To optimize NPS authentication and authorization response times and minimize network traffic, install NPS on a domain controller.
When universal principal names (UPNs) or Windows Server 2008 and Windows Server 2003 domains are used, NPS uses the global catalog to authenticate users. To minimize the time it takes to do this, install NPS on either a global catalog server or a server that is on the same subnet as the global catalog server.
When you have remote RADIUS server groups configured and, in NPS Connection Request Policies, you clear the Record accounting information on the servers in the following remote RADIUS server group check box, these groups are still sent network access server (NAS) start and stop notification messages. This creates unnecessary network traffic. To eliminate this traffic, disable NAS notification forwarding for individual servers in each remote RADIUS server group by clearing the Forward network start and stop notifications to this server check box.
Using NPS in large organizations
Following are the best practices for using NPS in large organizations.
Network Policy Server Windows 10
If you are using network policies to restrict access for all but certain groups, create a universal group for all of the users for whom you want to allow access, and then create a network policy that grants access for this universal group. Do not put all of your users directly into the universal group, especially if you have a large number of them on your network. Instead, create separate groups that are members of the universal group, and add users to those groups.
Use a user principal name to refer to users whenever possible. A user can have the same user principal name regardless of domain membership. This practice provides scalability that might be required in organizations with a large number of domains.
If you installed Network Policy Server (NPS) on a computer other than a domain controller and the NPS is receiving a large number of authentication requests per second, you can improve NPS performance by increasing the number of concurrent authentications allowed between the NPS and the domain controller. For more information, see Increase Concurrent Authentications Processed by NPS.
Security issues
Microsoft Network Policy Server Mac Authentication Download
Following are the best practices for reducing security issues.
When you are administering a NPS remotely, do not send sensitive or confidential data (for example, shared secrets or passwords) over the network in plaintext. There are two recommended methods for remote administration of NPSs:
Microsoft Network Client
Use Remote Desktop Services to access the NPS. When you use Remote Desktop Services, data is not sent between client and server. Only the user interface of the server (for example, the operating system desktop and NPS console image) is sent to the Remote Desktop Services client, which is named Remote Desktop Connection in Windows速 10. The client sends keyboard and mouse input, which is processed locally by the server that has Remote Desktop Services enabled. When Remote Desktop Services users log on, they can view only their individual client sessions, which are managed by the server and are independent of each other. In addition, Remote Desktop Connection provides 128-bit encryption between client and server.
Use Internet Protocol security (IPsec) to encrypt confidential data. You can use IPsec to encrypt communication between the NPS and the remote client computer that you are using to administer NPS. To administer the server remotely, you can install the Remote Server Administration Tools for Windows 10 on the client computer. After installation, use the Microsoft Management Console (MMC) to add the NPS snap-in to the console.
Important
You can install Remote Server Administration Tools for Windows 10 only on the full release of Windows 10 Professional or Windows 10 Enterprise.
Windows Server Network Policy Server
For more information about NPS, see Network Policy Server (NPS).